Azo Dyes are a fascinating group of synthetic dyes that are commonly used to add color to a wide array of products, from textiles to food and pharmaceuticals. Known for their vibrant hues and cost-effectiveness, azo dyes have been a mainstay in industries around the globe for decades. How are they used, and what safety considerations are associated with them.
What are Azo Dyes?
Azo dyes are synthetic colors that contain one or more azo groups (-N=N-), which create vivid colors when attached to aromatic compounds. The diversity in these compounds means that azo dyes can produce a range of colors from yellow and orange to deep red, blue and even green. These dyes are typically synthesized through chemical reactions involving aromatic compounds, making them a flexible choice for industries requiring a broad palette of colors.
Common Uses of Azo Dyes ¹
Azo dyes are used in various sectors because of their color intensity, durability and versatility. Here’s a closer look at their applications:
- Textiles: One of the largest uses of azo dyes is in the textile industry, where they color fabrics like cotton, wool and silk. These dyes offer excellent fastness, meaning they maintain their color even after washing and exposure to the sunlight.
- Food Coloring: Some azo dyes, such as tartrazine and sunset yellow, are used to make food colorants. These dyes help make foods appear more vibrant, enhancing consumer appeal. While synthetic, many food-grade azo dyes have been approved by regulatory agencies, although certain dyes are restricted in certain regions.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care: Azo dyes are also popular in the cosmetics industry, used in everything from lipstick to eyeshadow to create bright, bold colors.
- Pharmaceuticals: In the pharmaceutical industry, azo dyes are used for coloring tablets and capsules, making it easier for patients to differentiate between different types of medication.
Regulatory and Safety Standards of Azo Dyes ³
- European Union: The EU has some of the strictest regulations on azo dyes, especially those that can release carcinogenic aromatic amines. Specific dyes are banned in consumer products like clothing and toys, ensuring safer exposure.
- United States: The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved certain azo dyes for food, drug and cosmetic use, but only after thorough safety testing. The FDA also requires clear labeling for products containing those dyes.
- International Organization for Standardization: The ISO provides guidelines for the safe manufacturing and the use of azo dyes in various industries. This helps businesses maintain safety standards and avoid harmful environmental impacts.
Southampton Study ²
The University of Southampton did a study which reported evidence of increased levels of hyperactivity in young children when consuming beverages containing artificial food colors and the preservative sodium benzoate.
Study Design:
- Three separate groups of preschoolers ages 3-5 years old
- The drinks consumed in the study were of the two compositions:
- Granulated sugar, artificial colors and sodium benzoate
- Fruit juice containing natural sugars, vitamins and minerals
- Hyperactivity was then monitored
- Indicated by increased movement, impulsivity and inattention
- Study design was not based on a rating scale, no other diagnostic assessments were done
- One beverage was consumed everyday over a six-week period
The study DID NOT conclude that removing the additives studied will prevent hyperactive disorders.
European Food Safety Authority Evaluates Study:
- Found significant flaws in the study
- The artificial test mixtures were combinations of multiple food colors and sodium benzoate. Meaning the additives responsible could not be directly pinpointed.
- There was an overall lack of consistency in the results found. “The effects observed were not consistent between the two age groups and/or mixtures tested.”
- There was an absence of information on clinical significance of the behavioral changes
- Overall, the EFSA concluded that the study COULD NOT be used as a basis for altering the Acceptable Daily Intake of the additives tested.
*Acceptable Daily Intake– The recommended amount of a specific substance that can be ingested daily, over a lifetime without causing any appreciable health risks.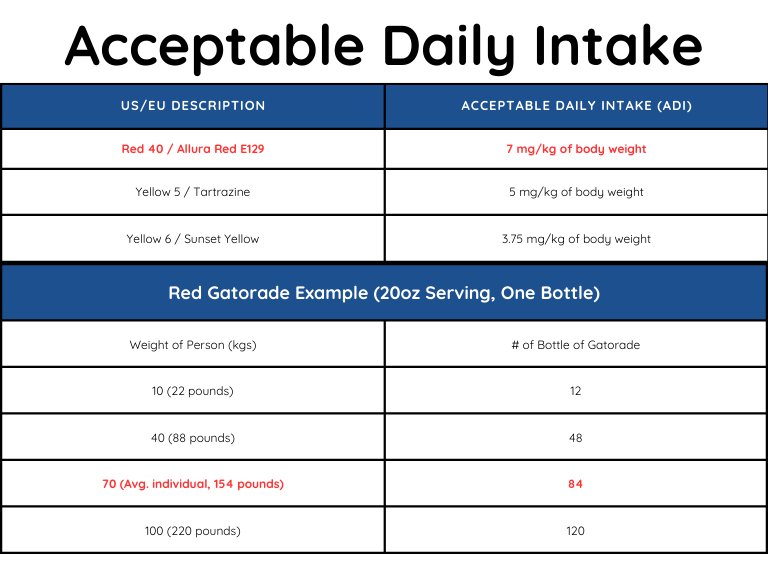
Quality Assurance
Here at Sensient, we pride ourselves on working to exceed industry standards for product quality, safety, and security. We maintain Good Manufacturing Practices and food safety standards to help ensure that our production processes are safe, from the arrival of raw materials to the shipment of our finished products. Additionally, every batch of synthetic colors made gets sent to the FDA for inspection to ensure safety.
If you are needing assistance with synthetic colors, please reach out and a member of our team will get in touch with you.
Sources:
1. Heliyon. 2020 Jan 31;6(1):e03271. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03271
2. EFSA evaluates Southampton Study on food additives and child behaviour. European Food Safety Authority. (2008, March 14). https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/news/efsa-evaluates-southampton-study-food-additives-and-child-behaviour
3. https://www.compliancegate.com/azo-dye-regulations-european-union/
Take It For A Test drive!
Requesting a sample from us is easy. We'll get it to you fast and with the support you need.
